Shipping Cost: How Much Will It Cost to Transport Goods? Breakdown & Guide
August 18, 2025
AAJ Swift

When it comes to shipping, the price can range from tens of rupees for small packages to thousands of rupees for large freight.
The cost of transporting goods usually falls between ₹5 to ₹10 per kg for small local deliveries. For larger ones, such as trucks, the shipping cost jumps to ₹10 to ₹25 per kg.
However, there is more to it than determining the final transportation cost, and how you can calculate total shipping based on the fuel, truck type, cargo weight, etc.
What Is A Shipping Cost?

In simpler terms, shipping cost is the total amount needed to move goods from one place to another. This mainly includes fuel, handling, port charges, and customs duties.
But when shipping costs include all costs, from getting goods from a business to their customers, it can be considered as a logistics shipping cost.
Difference Between Shipping Cost, Freight Charges, And Logistics Cost
Shipping costs include everything from moving goods from one place to another, i.e., transport, handling, and regulatory fees.
Freight charges only include the basic transport rate without including insurance. The LTL freight shipping cost actually depends on moving cargo by sea, air, or land.
Logistics costs stretch wider and include warehousing, inventory, order processing, order fulfillment, and their distribution and returns costs.
Why Understanding Shipping Costs Matters

Shipping cost is one of the most determining factors that can shrink your profit if you don't analyse it better.
A. Impact on Profitability, Pricing, and Satisfaction
While talking about shipping cost, it usually takes about 10-25% of the total product costs. So, they have only two options: either eat the cost or pass it to customers.
So, choosing the best logistics and transportation at a reasonable price helps businesses to get higher margins.
Example: Let's say a small headphone company sells headphones for ₹1000, and the shipping cost is ₹100. So, they can:
- Absorb costs: Sell for ₹1100 with "free" shipping
- Pass through: Sell for ₹1000 plus ₹100 shipping
- Split difference: Sell for ₹1050 with ₹50 shipping
B. Importance For E-commerce, Manufacturing, and D2C Brands
Based on the market, they sell products too; different businesses face different shipping headaches.
- E-commerce businesses mainly look for logistics that offer speed shipping and competitive prices. For example, Flipkart prioritizes fast shipping.
- Manufacturers ship heavy and large-volume stuff in big batches. It is also called commercial shipping or B2B shipping.
- D2C brands try to balance between a greater brand experience with sensible shipping costs.
How To Calculate Shipping Cost: Methods & Tools
There are two ways to calculate shipping cost: (a) manually and (b) using an online shipping rate calculator.
A. Manual Calculation
For the calculation, you need the following main things:
- Package weight (actual and volumetric). If you don't know the volumetric weight, calculate it using the formula: (Length x Width x Height) / Volume Factor.
- Pickup and delivery pin codes
- Type of Shipping service (Fast or standard shipping)
- Current carrier rates
- Applicable taxes and fees
Manual calculations work best for businesses that deal with the same type of item for the same destination. This gives a very close rough estimate that can be charged.
Manual Calculator Formula: (Weight x Distance x Rate/Km) + Handling + Tax
For example:
- 5 x 10 kg electronic package as 5 units using PTL
- Distance: 278 km
- Rate/km: ₹4 Per Km
- Handling: ₹550
- Tax: ₹300
Formula: (5 x 278 x 4) + 550 + 300 = ₹6,410
Limitations Of Manual Estimates
The following are some of the limitations of manual estimation:
- Rate changes: Carriers update prices without warning.
- Hidden surcharges: Fuel, residential, and remote area fees get overlooked.
- Zone complexity: Distance needs current zone maps.
- Service variations: Different speeds mean different formulas.
B. Online Shipping Rate Calculators
It is very hard to calculate the rate of modern freight using old-school calculators. Here are some of the popular online calculator types:
- Carrier websites: UPS, FedEx, AAJSwift, DHL
- Third-party platforms: Shippo, Easyship, and ShipStation compare multiple carriers
- E-commerce integrations: Shopify and WooCommerce have their own built-in rate tools.
So, using these advanced calculators, you can get very accurate quotes for your shipments.
How to use AAJ Swift Online Shipping Rate Calculator
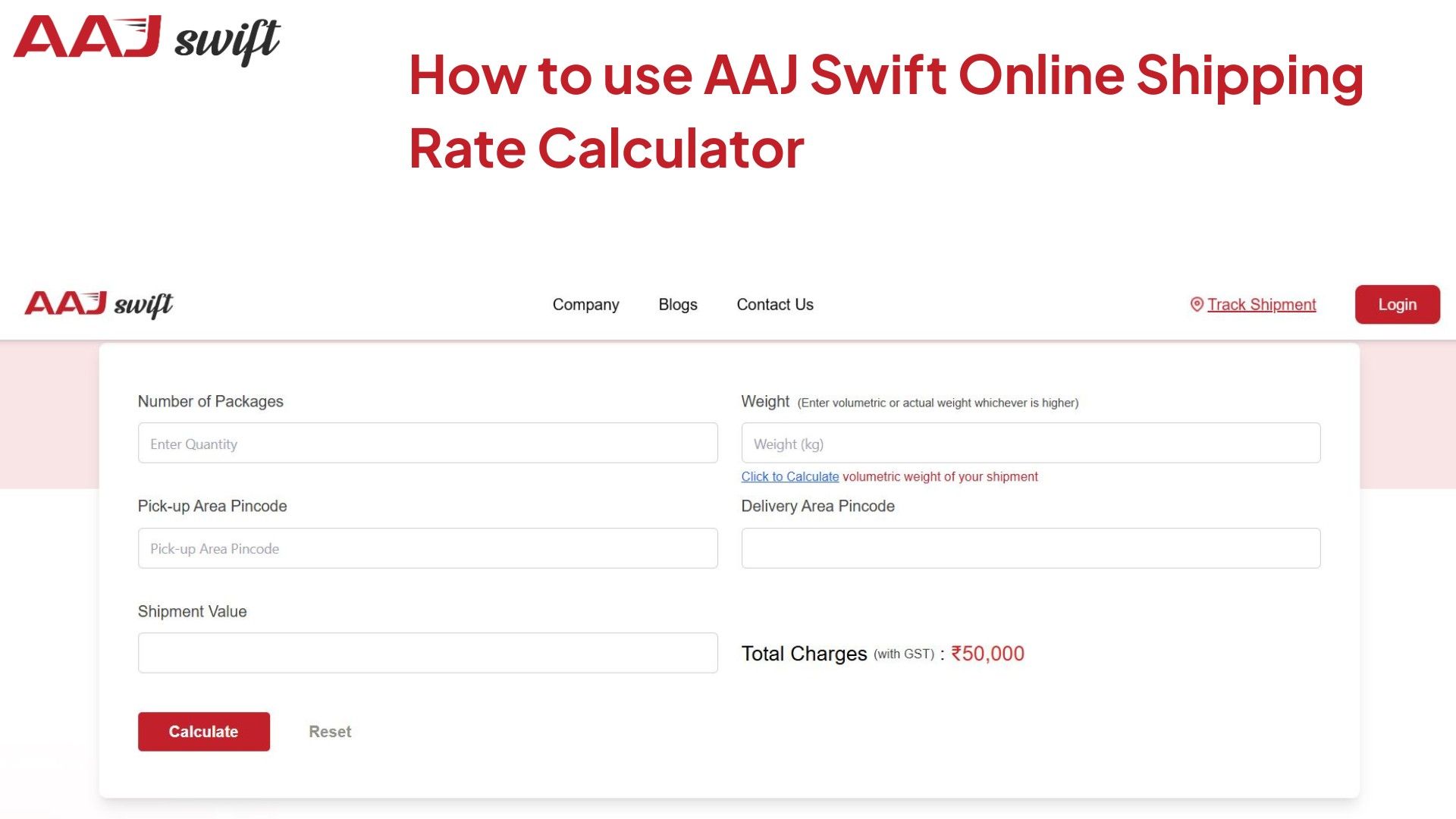
The following are the step-by-step method of using the AAJ Swift shipping rate online calculator.
- Number of Packages: Enter the total number of items needed to ship.
- Weight: Enter actual weight or volumetric weight (whichever value is higher). If you're not familiar with volumetric weight, you can calculate it by clicking the button below the box.
- Pickup Pincode: Eg, for Delhi, write pin code 110001
- Delivery Pincode: Enter the destination code, for example, for Mumbai 400001.
- Shipment Value: Enter the total value of your shipment and click on the calculate button.
Factors That Affect Shipping Costs

Now, let’s talk in detail what are the major factors that govern the shipping costs:
1. Mode of Transport
Transportation mode is one of the main factors that impact the cost of shipping goods. Below are the modes of transport with their cost structure.
- Air Freight: Most expensive but fastest, ideal for urgent or valuable items.
- Ocean Shipping: Cheapest for large and heavy loads over long distances, mainly for importing and exporting between countries.
- Rail Transport: Cheapest for heavy to small goods, but only where rails are available.
- Road Transport: It offers the most flexibility and also makes possible door-to-door delivery, and the major price contributing factors are fuel and distance.
- Intermodal Shipping: Combines different transport types (e.g., truck, rail, and truck) to optimize cost and time.
2. Shipment Weight & Dimensions
- Actual vs. Volumetric Weight: Most of the carriers charge based on whether the item has more weight (actual weight) or takes more space in trucks (volumetric weight).
- Consolidation: Most of the logistic companies optimize space by shipping multiple items together using PTL transport loads or full truck loads.
3. Delivery Zones and Distance
- Shipping Zones: Companies use zones to define shipping costs based on distance. Longer distances (higher zones) mean higher costs.
- Additional charges: Extra charges apply to international and remote area or rural shipments, as well as to faster shipments (such as same-day delivery).
4. Customs, Duties, and Taxes
- International Shipments: Additional charges to customs duties, including import taxes and customs broker fees.
- Requires proper paperwork & documentation to safeguard your shipments against unnecessary delays and item seizures.
5. Packaging and Handling Charges
- Shipments such as fragile items or hazardous materials need extra care and training, which automatically increases the charges.
- Temperature-sensitive shipments require refrigerated trucks and warehouses, which also adds costs.
6. Surcharges
- Common surcharges include fuel surcharges and peak season surcharges, which can fluctuate with time and seasons.
- Remote area, faster delivery, and charges during the rainy season are commonly included nowadays.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Estimating Shipping Costs
- Ignoring Packaging Dimensions: Carriers charge by dimensional weight (called volumetric weight), not just by the actual weight. They choose whichever is higher.
- Not Checking For Surcharges: Look for hidden surcharges such as for fuel, residential delivery, and peak season deliveries.
- Forgetting About Reverse Logistics: Businesses should also be held accountable for deciding how to handle returns and should use the same transport company for returns.
- Relying solely on flat-rate: You can lose your profits if you always stick to flat-rate shipping models or optimize your plan accordingly.
- Not reviewing rate slabs regularly: Shipping rates and surcharges change often, so make sure to check every time before making a deal with logistic companies.
Tips To Reduce Shipping And Logistics Costs
- Bulk Shipping Discounts: Bulk ordering increases per-item charges.
- Using Third-Party Logistics (3PL): Partnering with 3PL services can not only give faster deliveries but also offer a very competitive price if your shipment is less than a full truck load.
- Rate Negotiation With Carriers: The better you are at negotiating, the better you cut extra shipping and transport costs.
- Zone-Skipping Strategies: Saves money by sharing loads to regional hubs and then finally shipping to customers.
- Cross-Docking: Cross-docking reduces the storage of inventory in between. This cuts the warehousing storage cost.
With that, I hope you get how shipping costs are calculated and how you can do the same. If you need help finding shipping costs for your inventory, simply contact us with your details, and we'll provide the best market shipping price.

