
Transportation is the key to moving any item from one place to another. It connects suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers across the nation.
In India, all major transportation modes are available, i.e., road, rail, air, and waterways. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. However, they are the backbone of India's economy. So, the key is balancing between the cost and the service quality that it offers.
Understanding Transportation in the Supply Chain
Transportation is a major lever for cost, delivery speed, and reliability. In many sectors, transportation accounts for a significant portion of the total cost, so running it efficiently is crucial.
Common transportation modes:
- Road (Truck): Flexible, great for short and medium hops. Handles all sorts of cargo.
- Rail: Cheap for big, heavy loads over long distances.
- Air: Fastest out there, but pricey. Best for urgent or high-value shipments.
- Sea (Ocean): For huge volumes of global trade.
- Pipeline: For liquids and gases, this is a niche but efficient for those.
Modern technologies such as Transportation Management Systems (TMS) provide better route planning and shipment tracking. Additionally, sustainability promotes the use of electric vehicles and cross-docking, which minimizes carbon emissions.
Why Transportation Is Critical For Indian Businesses
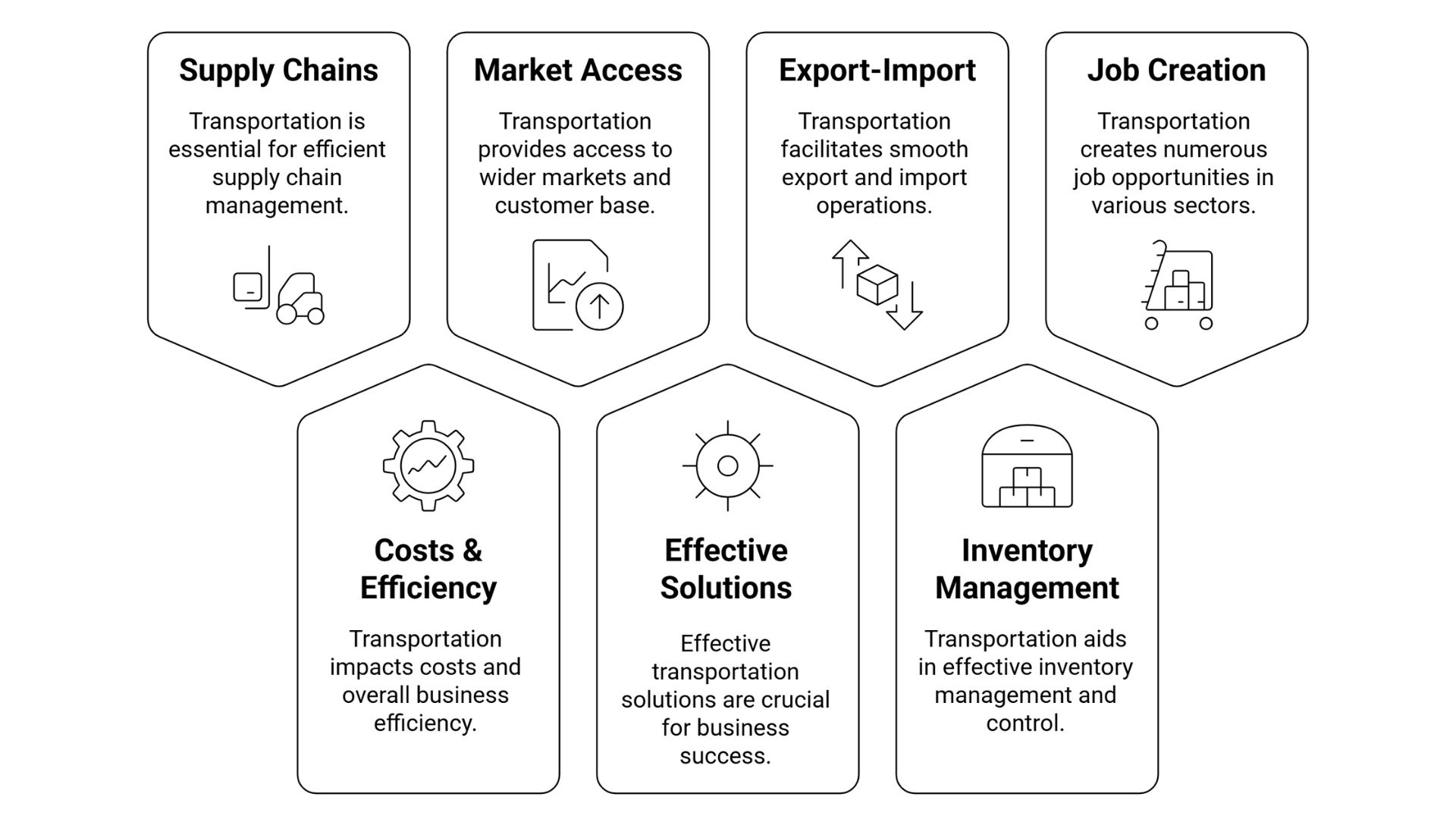
These are the reasons why transportation is important for Indian businesses:
- Supply Chains: Transportation is the network that joins manufacturers to their consumers with a reliable transportation network.
- Costs & Efficiency: With the latest technology and transport solutions, businesses now have more options to choose the best transportation and reliable logistics company as per their needs and budget.
- Market Access: It bridges rural businesses with city buyers across diverse geographical regions and ensures efficient distribution.
- Effective transportation solutions: The following are key benefits of effective transportation for businesses.
- Export-Import Operation: More than 90% of goods sold in India or internationally are only possible through transportation networks and logistics partners that directly support foreign exchange earnings.
- Inventory Management: Transportation, when coupled with order fulfillment services that modern logistics companies offer. Business now focuses on their products, and logistics companies manage all inventory, delivery, and returns.
- Job Creation: There are lots of jobs associated with transportation, mainly as truckers, transportation planners, logistics coordinators, etc.
Types Of Transportation Strategies In India
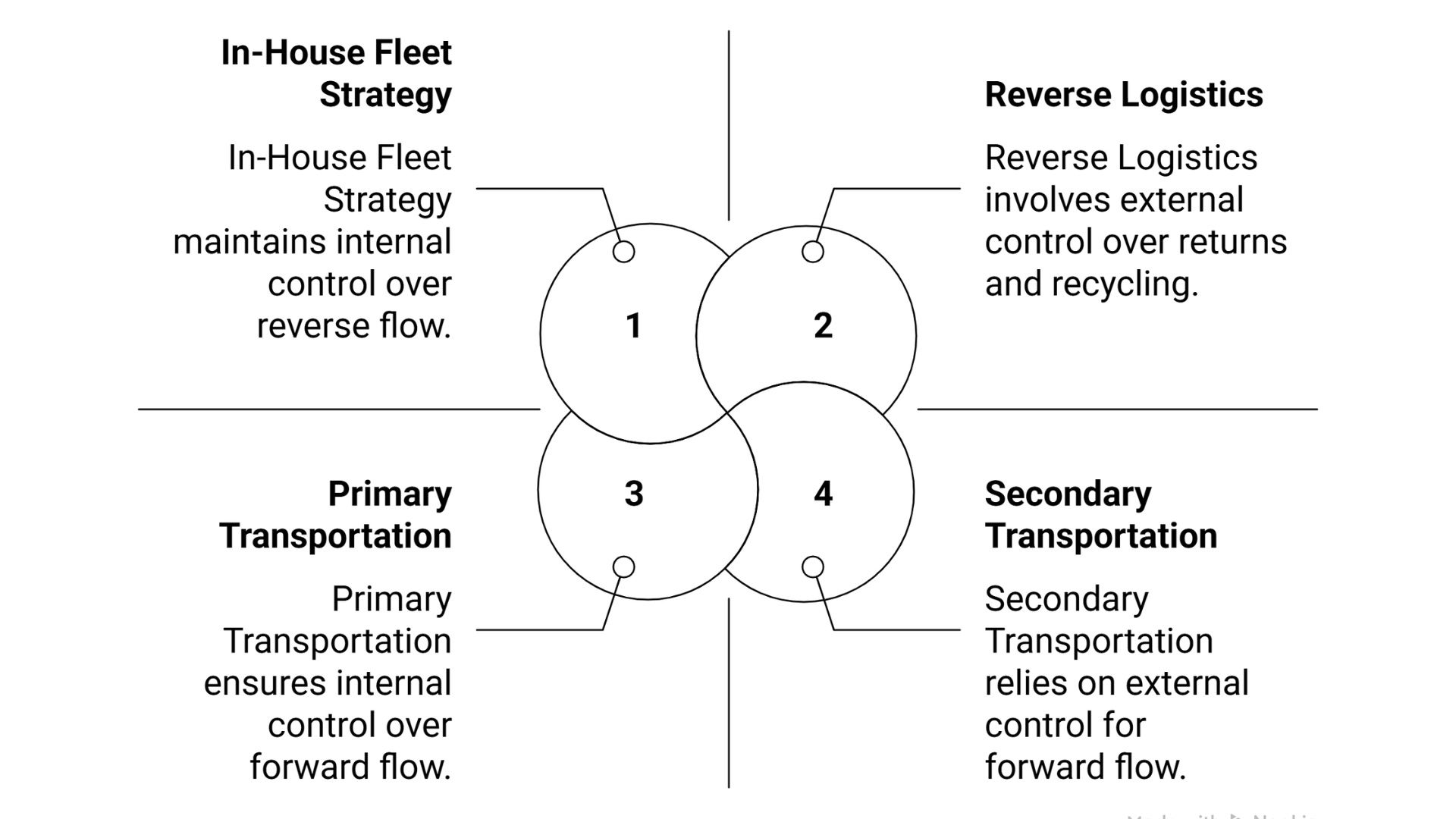
India's supply chain utilizes various modes of transportation that not only reduce costs but also increase efficiency.
1. Primary Transportation (Factory to Warehouse)
Primary transportation majorly deals with the bulk movement of goods from manufacturers to distribution centers or warehouses. Transportation (majorly) included in this sector are road, rail, and coastal shipping.
Here, companies prefer full truckload (FTL) shipments and dedicated routes to minimize shipping costs.
2. Secondary Transportation (DC to Retailer/Customer)
Goods are mainly termed as inventory in secondary transportation. Here, inventory is moved from warehouses/distribution centers to retailers or directly to end customers.
They mainly include smaller vehicles, such as vans, mini-trucks, and bikes, with a Less-than-Truckload (LTL) shipments approach.
The primary focus of this section is speed and reliability, enabling end customers to receive products within a specified time frame.
3. Reverse Logistics (Returns & Recycling)
About 1-3% of e-commerce goods are returned. So, to handle returns, there must be a well-set procedure to get faster returns. This sector also includes the fulfillment of warranty claims and recycling.
Note: Always choose a logistics company that consolidates returns for you, in addition to delivering them.
4. 3PL vs In-House Fleet Strategy
Third-party logistics (3PL) solutions provide scale, flexibility, expertise, and a network advantage to deliver faster with reasonable pricing, but schedules must be made in advance.
While in-house fleets offer more control and flexibility when shipping without prior notice, they also require more oversight and management. However, it needs a significant up-front cost.
The best model: Many businesses adopted a hybrid model that uses both in-house fleets and 3PLs to take advantage of vast networks and balance costs.
Cost Factors In Transportation
Transportation costs in India depend on the distance travelled, the type of cargo being carried, and the mode of transportation chosen. Here are all the factors that contribute to the cost of transportation:
- Freight Rates By Mode: Freight rates differ as you choose among different modes of transportation. Air freight is super expensive, while roads offer flexible and quick regional delivery.
- Fuel and Toll Costs: Fuel eats about 20% to 30% of the transportation budget. Additionally, the tolls on highways also add to the cost of every trip.
- Packaging and Handling: For moving goods, proper packaging is required to keep them safe. Packaging materials, such as wooden crates, corrugated boxes, pallets, and custom packaging for fragile items, as well as their handling, also increase the cost.
- Loading/Unloading Charges: It depends on the cargo type, its volume, and the frequency of loading/unloading. For smaller shipments, manual handling is sufficient, while for large warehouses and ports, mechanized systems are required.
- Transit Insurance: It is a must to have to prevent your goods from loss or damage during transit. Premium depends on what you're shipping, the worth of the inventory, the route, and the mode of transport.
Best Practices For Efficient Transportation
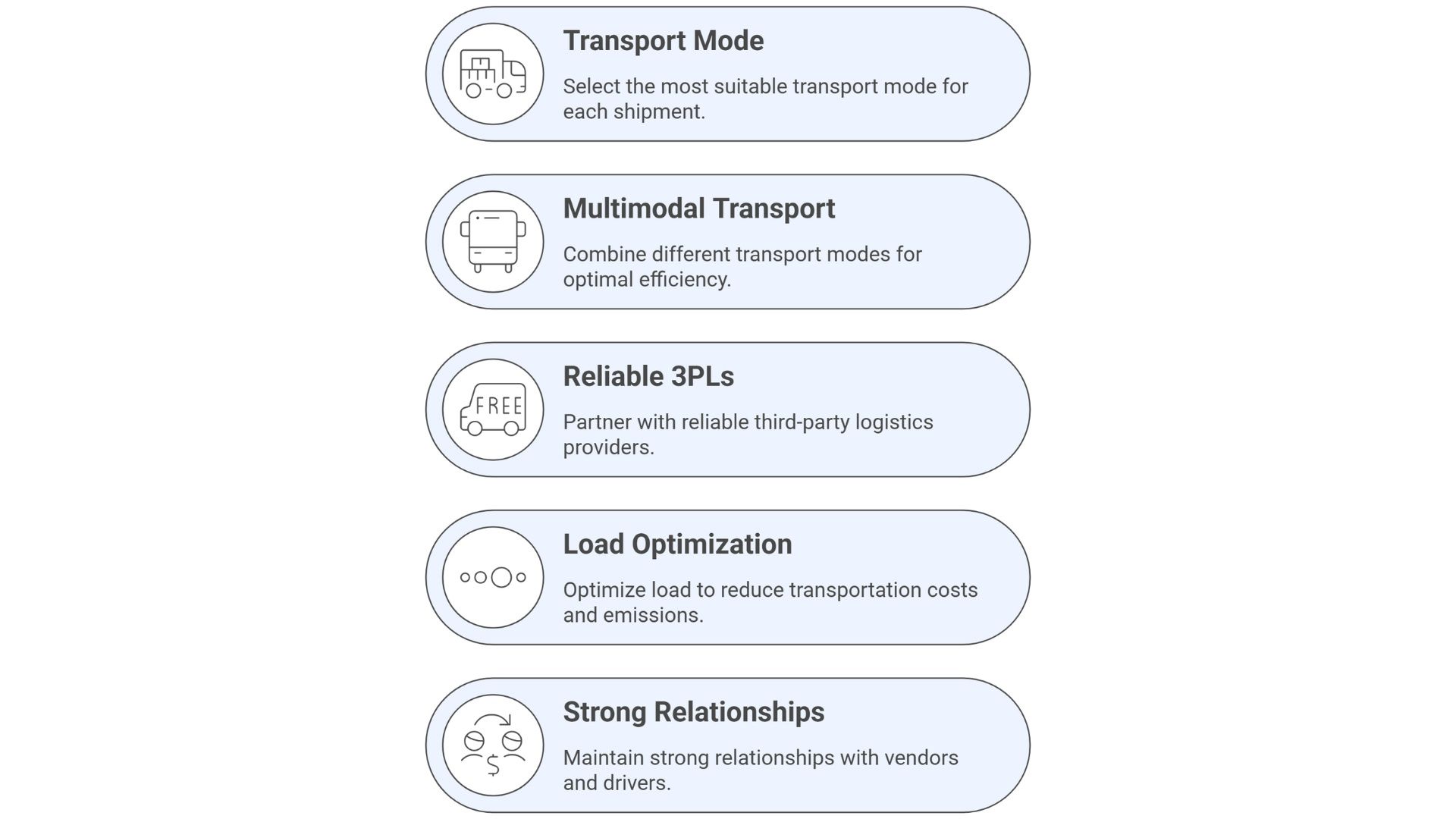
Optimizing transportation needs to address a few issues. Here are some of the best practices for efficient transportation.
- Choosing the right transport mode: Based on the product you ship and urgency, choose the best transportation mode. For example, perishable goods usually need road or air transport for speed, while rail or coastal shipping is far cheaper but deals in bulk.
- Leveraging Multimodal Transport: Using two or more modes of transportation is called multimodal transportation. This lowers the per-unit transport cost and makes transportation more efficient.
- Partnering With Reliable 3PLs: Third-party logistics (3PL) services bring expertise, warehousing, and a network of solid transportation routes that most businesses need for faster and reliable delivery without building their own. Note: A good 3PL provider should offer pan-India reach, fleet quality, and on-time delivery.
- Implementing Load Optimization: Load optimization simply means a vehicle is packed with its 100% of loading capacity (either by actual weight or volumetric weight). This means you need fewer trips, less fuel, and faster deliveries.
- Maintaining Strong Vendor and Driver Relationships: Having good communication and relationships means you have fewer headaches when things go south. So, be in touch with your vendors to set an expectation for delivery times and packaging.
Finally, with proper transportation planning, a business can boost its service quality along with reliability. Thus, for any business in the Indian supply chain, transportation plays a crucial role in customer satisfaction and order fulfillment.


