
India's bulk shipping moves more than 1.2 billion tons of cargo every year. In fact, over 60% of the world's overseas trade is in bulk cargo. So, what is really bulk shipping?
Bulk shipment simply refers to the movement of goods in large volumes, usually unpacked, such as raw materials or liquids, using vessels, trucks, or rail cars. It involves special equipment, and handling is completely different from regular freight.
So, if you're running a business and want to ship in bulk, then knowing its types, costs, and logistics process can save you a lot of money and headaches. With this post, you are going to know more about the bulk shipping industry and its types, and how you can choose the best bulk shipping and B2B transportation company for your business.
What is Bulk Shipment?
Bulk shipment means to move large quantities without putting goods into boxes or bags; instead, they are directly loaded into ships, rails, or special trucks.
So what's the need for special containers? Because for bulk shipping, cargo is usually in tons, and for that, cargo ships, rails, and trucks would be the best choice. This also decreases the shipping cost per kg/unit.
That's why bulk shipping is among the cheapest ways of moving materials over long distances.
Industries Using Bulk Shipment
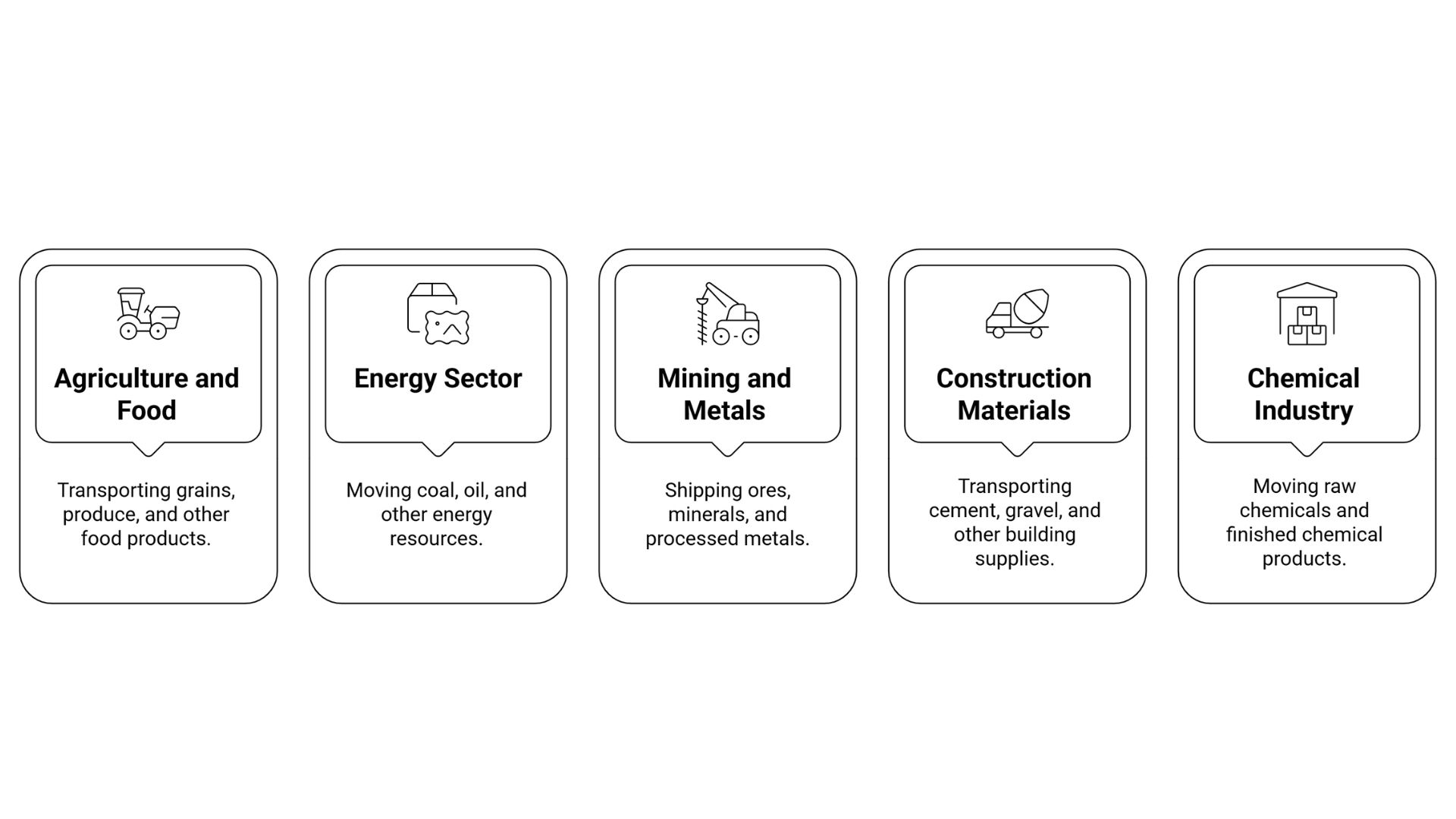
Almost all large industrial sectors in India use bulk shipments to keep production moving. Here is the list:
1. Agriculture and Food
- Wheat, corn, rice, and other grains
- Soybeans and other legumes
- Palm oil, soybean oil, and other cooking oils.
2. Energy Sector
- Coal for power plants
- Crude oil and petroleum products
- Liquefied natural gas.
3. Mining and Metals
- Iron ore is used to make steel
- Copper, bauxite, and nickel ores
- Salt and other minerals.
4. Construction Materials
- Sand and gravel
- Cement powder
- Stone and aggregate materials.
5. Chemical Industry
- Industrial chemicals
- Fertilizers and ammonia
- Plastic pellets and raw materials.
Bulk Shipping Vs Containerized Vs Parcel Shipping
Bulk vs. Part-Truckload (PTL) or LTL Logistics
Different Types of Bulk Shipment
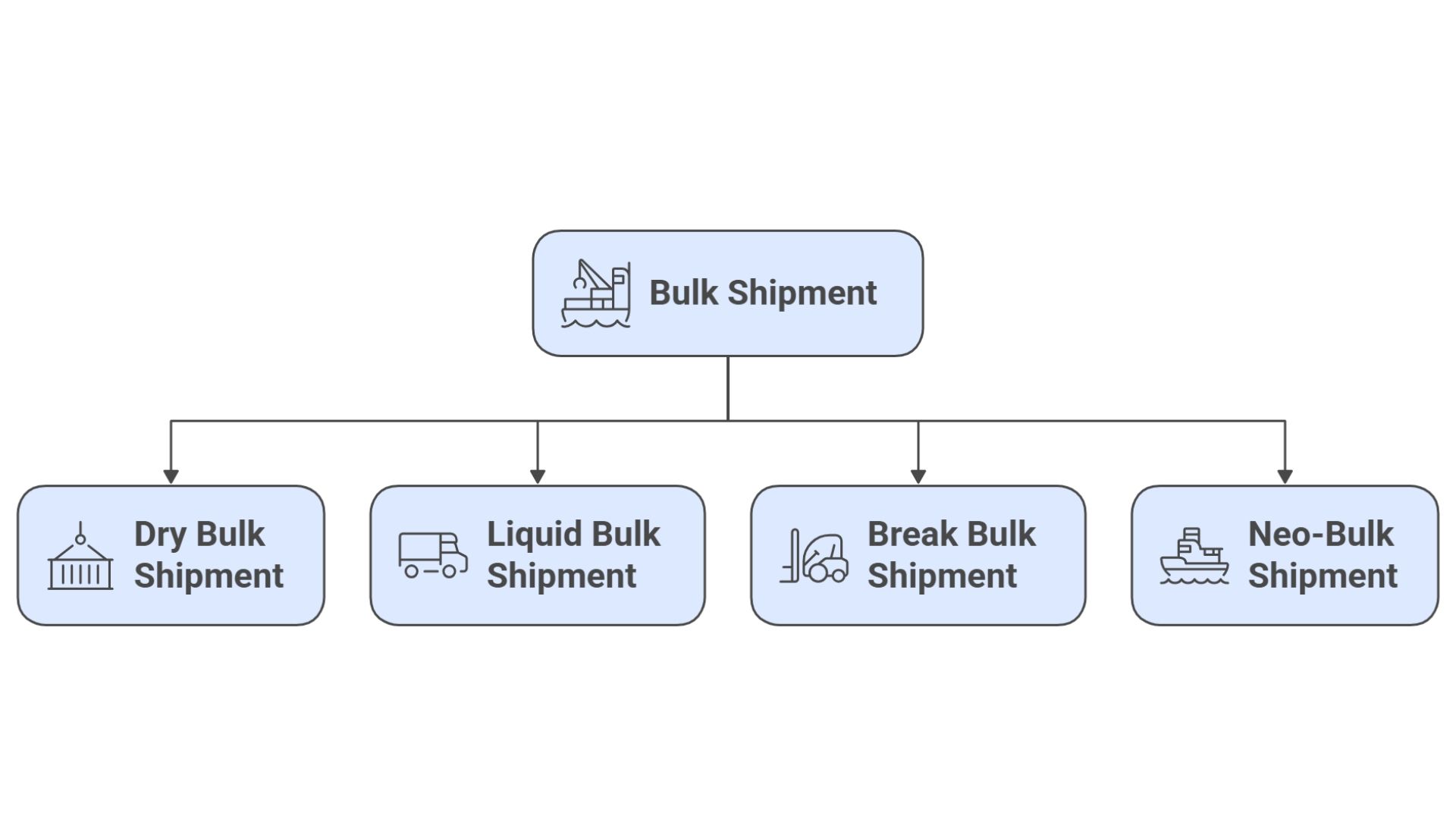
A bulk shipment can be divided into four main types. These are:
1. Dry Bulk Shipment
It is the classic type in which solid goods pour easily. Trains or ships dump these goods into big holds. They are mainly transported between the mining/production site to factories.
Common dry bulk goods include:
- Grains include wheat, corn, and soybeans
- Coal and iron ore
- Cement and fertilizers
- Sand and salt.
2. Liquid Bulk Shipment
They use special high-grade metal containers and ship with separating tanks that keep everything safe and intact.
Liquid bulk examples are:
- Crude oil and gasoline
- Chemicals and acids
- Vegetable oils
- Liquid natural gas.
3. Break Bulk Shipment
It refers to cargo that is loaded piece by piece and usually too large or irregularly shaped for standard containers and shipping methods. These things need special handling, but move in large quantities.
Break bulk examples are:
- Heavy construction equipment
- Bagged rice or coffee
- Large project pieces
- Palletized products.
4. Neo-Bulk Shipment
It offers a middle ground for prepacked cargo or large goods that need to be shipped in large bulk quantities.
Neo-bulk cargo includes moving:
- Cars and trucks
- Steel coils and pipes
- Lumber and paper rolls
- The large machinery parts.
Common Bulk Shipping Methods & Equipment: Sea, Road, and Rail
From loading to shipping, bulk shipments require specialized equipment that can't be achieved with manual labor. Here is a list of common equipment for various B2B shipping methods.
1. Sea Freight
Following is the list of bulk carrier types by size:
- Handysize: 10,000-40,000 deadweight tons (dwt).
- Handymax/Supramax: 40,000-65,000 dwt.
- Panamax: 65,000-85,000 dwt.
- Post-Panamax: 85,000-120,000 dwt.
- Capesize: 120,000-220,000 dwt.
Here is the list of loading/unloading equipment used in bulk sea shipping:
2. Rail Equipment for Bulk Shipments
3. Truck Equipment for Bulk Shipments
Key Factors That Affect Bulk Shipment Cost
The following are some of the factors responsible for the final shipping cost while doing bulk shipping:
- Type of Goods: Liquid bulk shipments generally cost more than dry goods, because special handling and equipment are required. If the cargo is hazardous to health, there will be additional safety fees.
- Volume and Weight: The heavier and bigger the shipment is, the more it will cost. High volumetric weight consumes more space and fuel, besides taking longer to handle.
- Distance and Routes: The longer the journey, the more expensive it is. Some routes are just better: less traffic, fewer delays, better infrastructure for handling goods.
- Loading and Unloading Charges: Each port has its own fee for loading cargo. Some large ports have fancy equipment that might load faster and may also cost more.
- Fuel Prices: As fuel costs fluctuate, so do the courier charges. So, in the case of an oil price hike, this simply means transport companies will pass it on to you as a fuel surcharge.
- Seasonal Demand: Peak season means everything is busier. This means everyone is fighting for space on ships, which also drives up the prices.
How to Ship Bulk Goods: Step-By-Step Process
For shipping in bulk, you need to plan ahead. Here is the quick guide on it:
- Choose Your Cargo: Identify the quantity type, weight, and shipping type needed for your first bulk shipment.
- Select Transportation Mode: Choose the transport mode that suits you best for your cargo type, such as:
- Sea freight is used when shipping large loads internationally.
- Rail for interstate.
- Truck for local or regional trips.
- Find the Right Carrier: Choose the best B2B transport service that has expertise in your cargo type and has a good business reputation.
- Get Proper Documentation: Most of the paperwork is handled by carriers, but you must cross-check it. Here are some:
- Bills of lading
- Commercial invoices
- Export/import permits
- Safety data sheets (for hazardous materials).
- Load the Cargo: Using equipment such as cranes, belts, or pumps to load your cargo. This increases workplace safety quickly.
- Track Your Shipment: Most B2B logistics service providers these days offer tracking, so you know the current status of your bulk shipment.
- Deliver at Destination: Unloading using a lot of the same gear as loading. The exact process again depends on your cargo type and what is available at the port or terminal.
- Final Distribution: You can now move your goods to the final stop using the local network, if needed.
How to Choose the Right Bulk Shipping Partner?
With the steady growth of global trade, selecting the right bulk shipping partner is important. So, one should look for:
- Cost transparency: Must offer a transparent breakdown of charges, including taxes.
- Proven track record: The company should have a reputation and have been doing business for 5 years.
- Global network: Must have a logistics partner in the region/country you want to serve or transport goods to.
- Specialized handling: Whether they have expertise in handling your goods type.
- Real-time tracking: Should offer a dashboard with real-time updates.
- Responsive customer support: It is a must; you should always go with companies that not only offer customer support but also have dedicated handling managers.
- Clear insurance terms: In case everything goes south.
Lastly, you must also inquire about the fuel surcharge policy and any other tech/special handling charges.
Ready to streamline your bulk shipping? Try AAJ Swift Logistics for reliable, efficient, and transparent PTL transport solutions based on your needs. Contact us today.


