Any company transporting goods, domestically or internationally, must be aware of the costs involved. Questions like how much it takes to send a product from Place A to Place B look simple at first, though they rarely stay that way. Once you start dissecting the logistics, the picture changes.
You must understand what transportation charges actually mean. For the uninitiated, they draw on dozens of moving variables every minute to arrive at a final rate. India's logistics sector already accounts for roughly 14% of the country's GDP, and a sizable portion of that is tied directly to road transport.
The number of toll plazas on national highways has grown steadily. They now contribute to toll collections crossing ₹50,000 crore annually. This has a direct effect on outbound and inbound freight forwarding expenses. Add to the fact that we now live in a world where customers want quick deliveries and clear pricing. For them, understanding how transportation costs behave is essential, as it directly influences profit margins, selling prices, and even customer trust.
If you run a business or work closely with one, then understanding the nuances behind transport charges becomes important. When you know where the money goes, you can plan better and make sound decisions for your organization.
What Are Transportation Charges
Basically, Transportation Costs are the amount a business pays to move its goods from any place, such as a factory or warehouse, to another destination. Some people tend to confuse this with freight charge, which is something entirely different.
Transport charges often include extra aspects like fuel surcharges, handling charges or even delivery to the last destination.
Every industry understands this cost in some form or another. This includes a lot of people from a textile exporter to a kirana distributor sending stock to tier 3 towns. You may even be a startup shipping candles via courier. Whoever you are, you pay something or the other to bring in movement for their goods.
Key Components of Transportation Charges in India
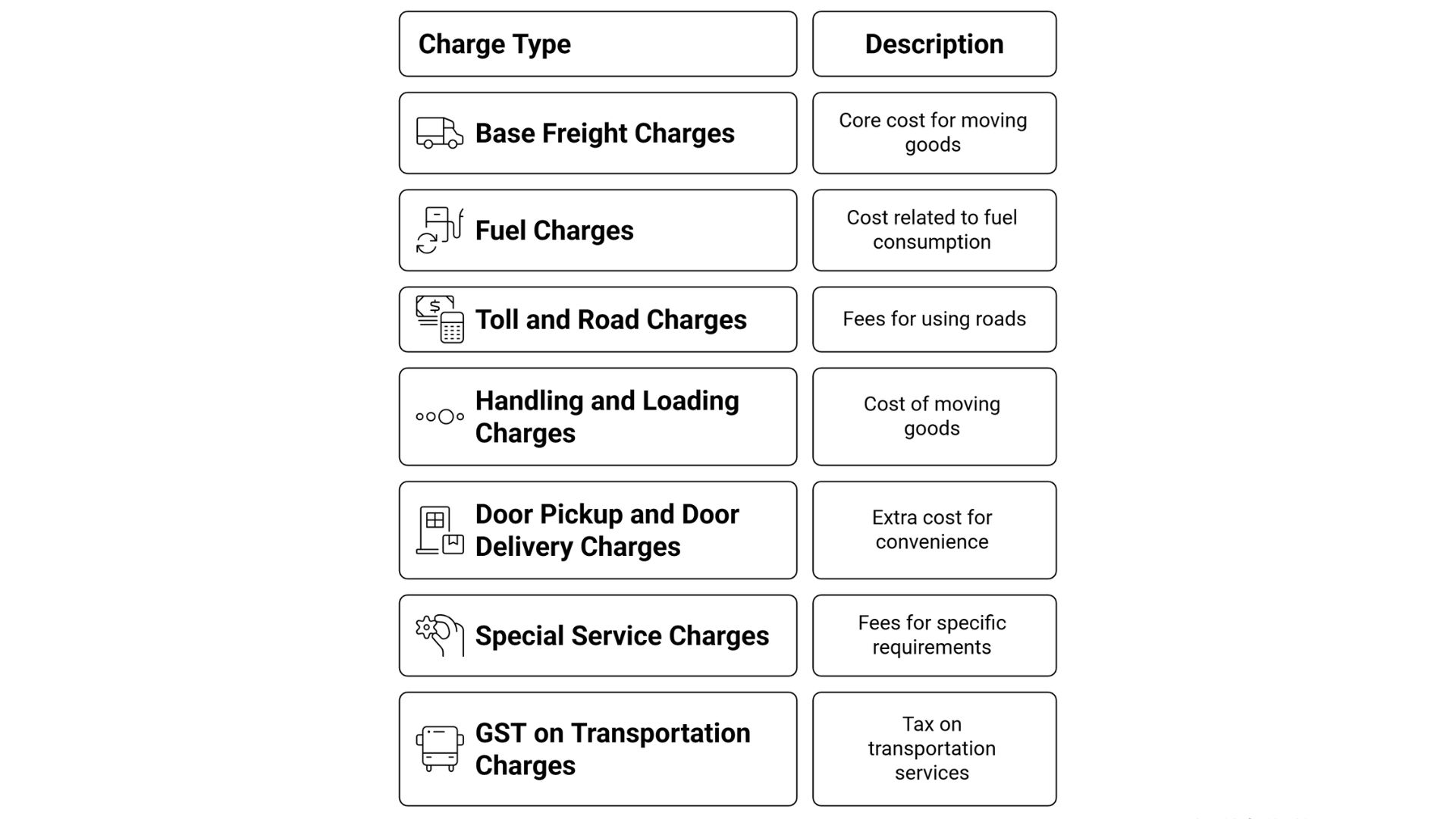
Transport billing rarely appears as a single line on a document. It is layered. Here is how the final figure builds up.
- Base Freight Charges: This forms the foundation. It is the cost to carry freight from the origin to the destination. Distance, network, and capacity affect it.
- Fuel Charges (Fuel Surcharge or FSC): Fuel never sits still. So, carriers add a percentage-based charge to offset changing diesel prices.
- Toll and Road Charges: Highways are faster, but every toll adds to the bill. India has thousands of toll plazas, and most carriers pass the cost to shippers.:
- Handling and Loading Charges: Loading labor at the pickup and unloading labor at the destination. Forklifts, Pallet trucks, it all counts.
- Door Pickup and Door Delivery Charges: Many transporters include only terminal-to-terminal in base freight. If you need pickup or doorstep drop, that is billed separately.
- Warehouse Handling and Storage: If goods wait a day or two inside a warehouse, storage fees may apply.
- Special Service Charges: Express delivery for urgent shipments. Reverse pickups for returns. Temperature-controlled movement for perishables. Even COD handling. All counted under extras.
- GST on Transportation Charges: GST and transport HSN code vary across transport services. Road transport often accounts for less than 5% of the operations of B2B transport companies. Air or ocean movement may differ. Knowing the slab helps with cost planning and input credit.
Factors That Influence Transportation Costs in India
Prices shift because they are tied to many real-world factors. Let's take a look at some of them.
- Mode of Transport: Road is common, though not always cheapest. Rail can save money across long distances. Air costs much more but saves time. The sea is slower, suited for bulk coastal cargo.
- Distance and Route Feasibility: Sometimes distance and route can be important factors. A short highway run can be easier than a tedious journey through a hilly region, for example.
- Weight and Volume of the Shipment: Whether you are charged the actual weight or volumetric weight (size & weight), you will be charged the greater of the two rates. A box of cotton is a box of cotton, regardless of its weight; it takes up space!
- Type of Goods: A carton of chips is treated differently from a carton of chemicals or machinery. Fragile goods are handled with care. Hazardous goods require paperwork and safe handling before shipment.
- Speed of Delivery: Same-day delivery, next-day delivery, and standard delivery service. Each speed has a price.
- Packaging Needs: Some products require extra cushions or reinforced crates.
- Seasonality and Demand: During the festive season months of October, November & December, there is pressure on capacity. Rates rise simply because space is tight.
- Carrier Approach and Service Level: Not all carriers charge the same way. Some carriers may spend considerable resources on technology and shipment tracking, while others take a no-frills approach.
Types of Transportation Charges Based on Business Model
Different businesses meet different cost patterns. Let's take a look at what they are.
- Business-to-Business transport charges: More often than not, you are moving larger shipments in bulk and are billed in slabs.
- eCommerce Transportation Charges: Parcels and rates include cash on delivery, pickups for returns, and delivery to the doorstep, a totally different cost basis.
- Retail and FMCG Distribution charges: There is typically a recurring route factor. Charged high frequency, mixed load deliveries to various stores.
- Export and Import transport charges: Moving freight from the factory premises to the port. Designated port charges and ocean freight on the international leg.
Transport Charges in India: Estimated Rates by Mode
Every mode carries a ballpark cost. Numbers swing, but here is a rough sense.
- Road Transport Charges: PTL logistics is charged per kg or per parcel, while FTL (Full truck load) depends on the truck size and route.
- Air Transport Charges: Premium charges for urgent or high-value cargo. Typically, they are priced on cost per kg.
- Rail Transport Charges: Cheaper cost over chains. Best for bulk goods, and some predictability in planning.
- Ocean Shipping Costs: Domestic shipping is helpful if time is flexible and costs are low.
How Transportation Charges Are Calculated
For a normal bill, there are a few simple steps that lead to the final number. It starts with checking the weight or the dimensional weight, and you have to use whichever is higher. After that, you add the slab rate per kilo or per shipment and then include the fuel surcharge.
The next step is to add handling or other service costs, and when that is done, you add taxes or GST. When all this is done, you get the full amount of the transport charges payable.
Why Transportation Charges Are Increasing in India
Some reasons are global. Some are tied to India's own growth path.
- Fuel inflation keeps pushing FSC higher.
- Toll density has shot up across new expressways.
- Fewer trained drivers join the workforce.
- ECommerce growth puts pressure on the last mile.
- Digital compliance measures, such as FASTag, GPS mandates, and e-way bill systems, add administrative costs.
Nothing moves as cheaply as before, which is why companies now track transportation costs much more closely.
How Businesses Can Reduce Transportation Costs
It is not always possible to cut rates, but cost control still has room for improvement. A Transport Management System can plan routes better and reduce empty returns. It offers visibility into where delays or excess spend creep in.
Shipment consolidation keeps trucks full rather than half-empty. A mix of Part load transport and FTL planning helps in many cases. Negotiating contracts works better when volumes are stable and predictable.
Logistics aggregators offer multiple carrier choices. You get access to different networks without managing each one. Improved packaging brings down volumetric weight. Less wasted space.
Switching to different modes of transport plans also helps. Send base load by rail. Use the road only for short distribution legs. Costs drop without slowing the supply chain.
How to Choose a Transport Partner in India
A good transport partner gives more than a truck and a bill. Look at the network first. A wide network keeps service consistent.
- PTL capability helps when your freight is not always full truckloads.
- Technology matters. Live tracking prevents guesswork.
- Check how pricing is structured. Transparent cost sheets prevent shock costs at month-end.
- Delivery performance says a lot. On-time delivery keeps customer promises intact.
Conclusion
Businesses no longer treat Transportation Charges as a simple bill to pay at the end of the month. They read it with care. Every line tells a story about time, fuel, workers, storage, and even weather.
When Transportation Costs rise, margins shrink. So the goal is not only to spend less, but to spend wisely. Choose logistics partners with reach. Build smarter freight plans. Keep shipments efficient.


